|
 Marasmius exustoides Marasmius exustoides
BiostatusPresent in region - Indigenous. Endemic
Images (click to enlarge)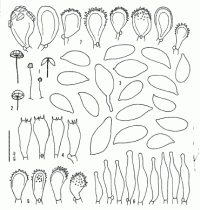
Caption: Fig. 12 (1-7). Marasmius exustoides Desjardin & E. Horak (PDD, holotype).- 1. Basidiomes.-
2. Basidiomes.(x3)- 3. Basidiospores.- 4. Basidia.- 5. Cheilocystidia a). 6. Cheilocystidia b).-7.
Pileipellis. | 
Owner: J.A. Cooper | 
Caption: scale=1mm
Owner: J.A. Cooper | 
Caption: cap rotalis cells, pilocystidia and spores.
Owner: J.A. Cooper | 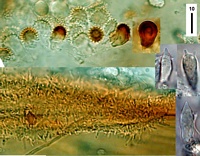
Caption: top: cheilocystidia (brown part of gill edge). Lower: caulocystidia. Right: basidia and hyaline cheilocystidia.
Owner: J.A. Cooper | 
Caption: Dried type specimen
Owner: Herb PDD |
Article: Desjardin, D.E.; Horak, E. (1997). Marasmius and Gloiocephala in the South Pacific Region: Papua New Guinea, New Caledonia, and New Zealand taxa. Bibliotheca Mycologica 168: 152 p.
Description: Pileus 2-3 mm diam, hemispherical to convex, disc not depressed, papilla absent, margin plicate and
scalloped; surface dull, dry, glabrous; evenly dark brown to dark reddish brown. Texture
membranaceous; context thin, concolorous with pileus surface.- Lamellae adnexed to almost
free, subdistant (610), lamellulae absent, ventricose, off-white; edges even, concolorous.-
Stipe10-25 x 0.2-0.4 mm, central, equal, wiry, tough, glabrous, polished, insititious; black
overall; rhizomorphs absent.- Odor and tastenot distinctive.
Basidiospores 8.5-11.5 x 4-5 µm, ellipsoid, sometimes slightly curved in profile, smooth, thin-walled, hyaline, inamyloid.- Basidia 18-22 x 8-10 µm, clavate, 4-spored, clamped.-
Cheilocystidiaof 2 types: a) scattered Rotalis-type cells 12-20 x 6-10 µm, broadly clavate,
apically brown; divergent setulae 1-3 x 1 µm, cylindrical; b) 25-32 x 5-7 µm, fusoid to lanceolate,
apex acute or subcapitate, hyaline, thin-walled.- Pleurocystidia absent. Pileipellis hymeniform,
slightly mottled, composed of Rotalis-type cells; main body 12-20 x 7-15 µm, clavate, thick-walled, brown to reddish brown; divergent setulae 1-3 x 1 µm, cylindrical; on pileus disc thick-walled, clavate pileocystidia projecting beyond the Rotalis-type cells, 30-50 x 10-20 µm, covered
with reddish brown, coarsely roughened, resinous incrustations.- Pileal and tramal tissue
inamyloid.- Stipe tissue monomitic; cortical hyphae parallel, cylindrical, smooth or rougened.-
Caulocystidia absent. Clamp connections present.
Habitat: Habit, habitat and distribution.- Solitary, in groups on rotting leaves of Cordyline (Agavaceae).
New Zealand.
Notes: Diagnostic features of Marasmius exustoides include the following: small, convex, plicate, dark
reddish brown pileus; non-collariate, non-marginate, subdistant, white lamellae; a relatively short,
glabrous, insititious, black stipe; basidiospores 8.5-11.0 x 4-5 µm; two types of cheilocystidia; a
pileus disc with clavate pileosclerocystidia covered with reddish brown, coarsely roughened,
resinous incrustations; smooth to roughened but non-setulose stipe cortical hyphae; and growth
on leaves of Cordyline. Marasmius exustoides is similar to M. exustus Berk. & M. A. Curtis, M.
crescentiae Murrill, M. minutus Peck, and M. kroumirensis (Pat.) Sacc. & Sydow. Marasmius
exustus, from the Bonin Islands, differs in forming much smaller basidiospores (6.5-8.0 x 4-5
µm), grows on dicotyledonous leaves, and lacks pileosclerocystidia on the pileus disc (Isotype,
FH!). Marasmius crescentiae, from South America and Papua New Guinea, differs in forming
paler and more yellowish brown pilei, smaller basidiospores (7.5-8.5 x 3.5-4.0 µm), has scattered
pleurocystidia, densely setulose stipe cortical hyphae, and fusoid-lageniform pileoleptocystidia
but no clavate pileosclerocystidia (Holotype, NY!). Marasmius minutus, from eastern North
America and Europe, differs in forming smaller basidiospores 6.0-9.5 x 3-4 µm, numerous
fusiform to lageniform pleurocystidia and pileoleptocystidia, setulose stipe cortical hyphae, and
grows on dicotyledonous debris (Holotype, NYS!). Marasmius kroumirensis, from northern
Africa, differs in forming only Rotalis-type cheilocystidia, and in having numerous fusiform to
lanceolate pleurocystidia. Other micromorphological data of M. kroumirensis are unavailable
because the species is known only from a single fragmented basidiome of the holotype specimen
(fide Pegler, 1966).
|