|
 Hypoderma obtectum Hypoderma obtectum
BiostatusPresent in region - Indigenous. Endemic
Images (click to enlarge)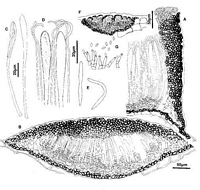
Caption: Fig. 9 Hypoderma obtectum: A, margin of ascoma in vertical section (PDD49257). B,
immature ascoma in vertical section (PDD 46712). C, asci (PDD 49256). D, apex of asci and
paraphyses (PDD49256). E, released ascospores (PDD 49256). F, conidio | 
Caption: Fig. 22 Hypoderma obtectum (PDD 49256). Macroscopic appearance of ascomata (x15). |
Article: Johnston, P.R. (1990). Rhytismataceae in New Zealand 3. The genus Hypoderma. New Zealand Journal of Botany 28(2): 159-183 (http://www.rsnz.org/publish/abstracts.php).
Description: Ascomata and conidiomata developing on fallen leaves, within pale, yellowish areas on host
leaf. Pale areas not associated with zone lines on Nothofagus, but when on Weinmannia
leaves often with broad, brown, diffuse, zone lines. In surface view ascomata 0.6-1.5 x 0.4-0.7 mm, broad-elliptic in outline with rounded ends. Unopened ascomata with uniformly shiny
black walls. Ascomata opening by single, longitudinal slit, edge of the opening lined with a
narrow differentiated zone, silver-grey when fresh, yellowish in dry specimens. Opened
ascomata and surrounding host tissue often covered with sparse or dense mat of fine, white to
yellow aerial hyphae. Conidiomata 0.2-0.3 mm diam., circular in outline, pale to dark brown
to black, pustulate.
Ascomata subcuticular. In vertical section upper wall of unopened ascomata up to 50 µm
thick, thinner toward the edges of the ascomata. Wall comprising mostly brown to pale
brown, angular cells, darker toward the outside of the wall. In the inner half of the wall, along
the future line of opening, is an ill-defined area of paler, thinner walled cells. Inside edge of
the wall is lined with an irregular, 1-cell-wide layer of hyaline, cylindric to globose cells. In
opened ascomata the upper wall is up to 80 µm thick near the ascomatal opening, becoming
gradually thinner toward the base. Upper wall comprising brown to dark brown, thick-walled,
globose to angular, 4-10 µm diam. cells. Exposed face of the broken upper wall is lined with
a layer of hyaline, thin-walled, cylindric, 15-25 x 3-4 µm cells. Lower wall 8-15 µm thick, of
2-3 layers of brown, thick-walled, cylindric to angular, 3-6 µm diam. cells.
Paraphyses 1-2 µm diam., circinate at apex, extending 5-10 µm beyond asci. Asci 110-155 x 8.5-10.5 µm, clavate-stipitate, tapering to rounded apex, wall undifferentiated at apex,
8-spored, spores confined to upper half of ascus. Ascospores 24-38 x 2.0-2.5 µm (average
32.8 x 2.1 µm), cylindric-bifusiform, apex rounded, tapering to base, slight constriction near
centre of the spore, hyaline, 0-septate, surrounded by narrow gelatinous sheath. Conidiomata
subcuticular. In vertical section upper wall more or less lacking, or up to 5-8 µm thick,
comprising dense, dark brown to black material with no obvious cellular structure. Lower
wall 10-15 µm thick, of 2-3 layers of dark brown, thick-walled, cylindric cells. Lower wall
lined with 2-3 layers of hyaline, thin-walled, angular cells on which the conidiogenous layer
develops. Columns of sterile cells may extent between the upper and lower wall near the
centre of the conidiomata. Conidiogenous cells 7.5-12.0 x 1.5-2.5 µm, more or less cylindric,
proliferation percurrent, wall of conidiogenous cell slightly thickened and often flaring at the
apical conidiogenous locus. Conidia 3-4 x 1-1.5 µm, cylindric, ends rounded, hyaline, 0-septate.
CHARACTERISTICS IN CULTURE: A few ascospores from PDD 43266 and PDD 46711
germinated on agar plates after48 hours. Colonies on OA 30-40 mm diam. after 8 weeks,
aerial mycelium grey, dense, cottony to felted, agar surface dark brown near centre of colony,
reddish toward edge with red pigment diffusing into agar around colony. Remaining sterile.
Habitat: Fallen leaves of Nothofagus truncata, Quintinia acutifolia, Q. serrata, and
Weinmannia racemosa, rare on Hebe stricta.
Distribution: Northland, Auckland, Coromandel, Gisborne, Taupo, Nelson,
Marlborough, Buller, Westland, Southland, Fiordland.
Notes: ETYMOLOGY: obtectum = covered over; refers to sparse layer of mycelium covering the
upper wall of the ascomata.
NOTES: H. obtectum is easily distinguished from other New Zealand species by the wispy,
yellow or white, aerial hyphae surrounding the ascomata, and by the size and distinctive shape
of its ascospores.
|