|
 Hypoderma bihospitum Hypoderma bihospitum
BiostatusPresent in region - Indigenous. Endemic
Images (click to enlarge)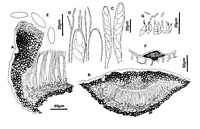
Caption: Fig.3 Hypoderma bihospitum: A, margin of ascoma in vertical section (PDD 46769). B,
immature ascoma in vertical section (PDD 46769). C, asci (PDD 49305). D, apex of asci and
paraphyses (PDD 49305), E, released ascospores (PDD 49305). F, con | 
Caption: Fig.16 Hypoderma bihospitum (PDD53886). Macroscopic appearance of ascomata (x15). |
Article: Johnston, P.R. (1990). Rhytismataceae in New Zealand 3. The genus Hypoderma. New Zealand Journal of Botany 28(2): 159-183 (http://www.rsnz.org/publish/abstracts.php).
Description: Ascomata and conidiomata developing on fallen leaves and dead inflorescence stems, within
pale, yellowish areas. These pale areas often surrounded by narrow, black zone lines. In
surface view ascomata 0.6-1.2 x 0.3-0.5 mm, broad-elliptic in outline with rounded ends.
Unopened ascomata with uniformly black walls. On Uncinia the edge of the ascomata is often
not sharply defined, with black stippling in the surrounding host tissue (see notes below).
Ascomata open by a single, longitudinal slit, the edge of the opening is lined with a narrow,
white, red-brown, or yellow-brown zone. Conidiomata 0.1-0.2 mm diam., circular in outline,
brown to dark brown, pustulate.
Ascomata subcuticular. In vertical section upper wall of unopened ascomata up to 30-40
µm wide, narrower toward edges, comprising mostly brown to dark brown, thick-walled cells,
darker and thicker-walled along the outside of the wall. In unopened ascomata there is a
group of thinner-walled, paler cells in the inner half of the wall along the future line of
opening. Inside edge of the wall is lined with a one cell wide layer of hyaline, thin-walled,
cylindric to globose cells. In opened ascomata the upper wall is up to 40-80 µm thick near the
ascomatal opening, becoming gradually narrower toward the base of the wall, comprising dark
brown, thick-walled, angular cells, or becoming very dark, with cellular structure . cured.
Exposed face of the broken upper wall is lined with a layer of cylindric, thin-walled, hyaline,
15-20 x 3-5 µm cells. Lower wall 10-15 µm thick, of 2-4 layers of brown, thick-walled,
angular to cylindric, 4-10 µm diam. cells.
Paraphyses 1-2 µm diam., undifferentiated or irregularly circinate at apex, embedded in
persistent gel, extending 15-20 µm beyond asci. Asci 80-130 x 11-16 µm, clavate, tapering to
broad, truncate to slightly rounded apex, indistinct central apical pore, 8-spored, spores
extending to base of ascus. ascospores 13-19 x 4.5-6.5 µm (average 15.1 x 5.2 µm), in face
view elliptic, uniform in shape to both ends, 0-septate, surrounded by a thick gelatinous
sheath.
Conidiomata subcuticular. In vertical section the upper wall is less than 5 µm thick, of
dense, dark brown material with no obvious cellular structure. Lower wall 3-5 µm thick, of 1-2 layers of brown, thick-walled, angular to cylindric cells. Lower wall is lined with 1-2 layers
of hyaline, thin-walled, cylindric cells on which the conidiogenous layer develops.
Conidiogenous cells 7-10 x 2-2.5 µm, more or less flask-shaped, tapering to apex proliferation
sympodial, often with two conidia held at apex. Conidia 4-5 x 1 µm, cylindric, straight, ends
rounded, 0-septate, hyaline.
CHARACTERISUCS IN CULTURE: Ascospores of PDD 45036 germinated on agar plates
after 48 hours. Colonies on OA over 85 mm diam. after 6 weeks, aerial mycelium sparse,
cottony, white, agar surface becoming dark brown. Black, globose conidiomata forming near
edge of the colony, breaking open to expose the conidial ooze. Conidiogenous cells 7-17 x 2-6 µm, with swollen base with more or less cylindric upper part, sympodial proliferation, often
with more than one conidium held at apex. Conidia 4.5-8 x 1-1.5 µm, cylindric, ends rounded,
straight, 0-septate, hyaline.
Habitat: Dead leaves and inflorescence stems of Anisotome spp. (Umbelliferae), and
Uncinia spp. (Cyperaccae).
Distribution: On Uncinia - Northland, Auckland, Coromandel, Taupo, Taranaki, Nelson.
On Anisotome - Taupo, Taranaki, Wellington, North Canterbury, Mid Canterbury.
Notes: ETYMOLOGY: bihospitum = of two hosts; refers to unusual host distribution of this
species.
NOTES: H. bihospitum can be distinguished from other New Zealand Hypoderma species by
ascospore size and shape, and by ascus shape. Hypoderma species typically have clavate-stipitate asci with an elongate, stalk-like base, with the ascospores confined to the upper part
of the ascus. Apart from ascus shape, all other characteristics of the hymenium, and of
ascomatal structure and pattern of ascomatal development, conform to the concept of
Hypoderma accepted in this study.
The host distribution of H. bihospitum is difficult to explain. When viewed in vertical
section the collections on Uncinia tend to have darker upper walls to the ascomata, and, in
unopened ascomata, a less well-developed paler zone along the future line of opening. The
stippled appearance of the host tissue surrounding the ascomata in the collections on Uncinia
is due to the stomatal cavities near the ascomata becoming packed full of dark fungal tissue,
and is a feature not found on the collections from Anisotome. Apart from these three
somewhat variable features, the collections on the different hosts are indistinguishable both
macro- and micromorphologically.
H. bihospitum is the only species of Rhytismataceae found on Anisotome, but both
Lophodermium unciniae Johnston and L. breve (Berkeley) de Notaris are also commonly
found on Uncinia (Johnston 1989).
|