|
 Moellerodiscus microcoprosmae Moellerodiscus microcoprosmae
SynonymsCiboria microcoprosmae
BiostatusPresent in region - Indigenous. Endemic
Images (click to enlarge)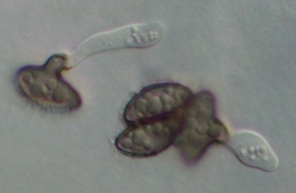
Caption: spores turn brown when germinating on agar
Owner: P.R. Johnston | 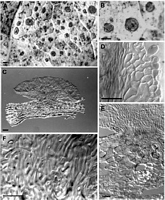
Caption: Fig. 5 Moellerodiscus microcoprosmae (A-B, PDD 58116; C-F,PDD 70137). A, macroscopic
appearance with numerous, small,round stromatic areas on a single leaf; B, macroscopic
appearance, detail of | 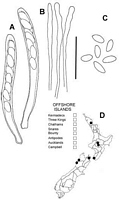
Caption: Fig. 6 Moellerodiscus microcoprosmae (PDD 70137). A, asci containing ascospores; B, apex
of paraphyses; C, released ascospores; D, distribution of collections e |
Article: Johnston, P.R. (2002). Three new species of Moellerodiscus (Helotiales, Rutstroemiaceae) from New Zealand. New Zealand Journal of Botany 40(1): 105-115 (http://www.rsnz.org/publish/abstracts.php).
Description: DESCRIPTION: Apothecia developing on both upper and lower surface of fallen leaves,
associated with numerous, small, (4-)7-10(-25) mm diam., more or less round stromatic
areas, leaf surface in these areas dark grey, margin marked by narrow black zone line, the
stromatic areas contain small, round dark spots from which the apothecia arise.
Apothecia erumpent from beneath epidermis, through what appear to be largely intact,
although empty, epidermalcells, arising directly from the mass of hyphae filling the leaf;
hyphae within host tissue packing the intercellular spaces, walls brown, highly
gelatinised, plant cells still evident amongst the hyphae, although partly crushed. Apothecia
0.2-0.3 mm diam.,cupulate, more or less sessile; disc plane, orange-yellow to reddish brown
when fresh, slightly darker, orange-brown when dry; receptacle concolorous with disc,
glabrous. Ascomata release yellow-brown pigment in KOH. Ectal excipulum up to 40 µm
thick, textura globosa to textura angularis with elements oriented more or less perpendicular to
receptacle surface, comprising angular to globose, 10-12.5 µm diam. cells with walls thick,
hyaline, refractive,outermost cells more or less free, containing bright red pigments.
Medullary excipulum comprising more or less parallel rows of hyphae 3-4 µm diam. with
walls thin, encrusted, pale brown to brown, nongelatinous (becoming gelatinous toward the
base of the stipe). Subhymenium textura intricata comprising hyphae 2.5-4.5 µm diam. with
walls brown,thin, nongelatinous. Paraphyses 1.5-2 µm diam., apex swollen to 2.5-4.5 µm
diam., unbranched, in water containing reddish pigments, changing to bright red in KOH, then
becoming colourless with addition of Melzer's reagent, about same length as asci. Asci
(60-)65-75(-80) x 7-7.5(-8.5) µm, cylindric to subclavate, tapering slightly to
subtruncate apex, wall thickened at apex, apical pore amyloid, faint reaction apart from two
intense spots on inside of wall, 8-spored, spores overlapping uniseriate, extending 50-60 µm
from ascus apex. Ascospores (7.5-)8-9(-9.5) x 3.5-4(-4.5) µm (x- 8.5 x 3.9 µm,n = 22),
oblong-elliptic, ends rounded, flattened one side, sometimes slightly curved, slightly wider
in upper half, 0-septate, wall hyaline, thin, smooth.
Notes: ETYMOLOGY: Refers to host substrate, and the small size of the apothecia compared with C.
coprosmae.
|