|
 Moellerodiscus griseliniae Moellerodiscus griseliniae
SynonymsCiboria griseliniae
BiostatusPresent in region - Indigenous. Endemic
Images (click to enlarge)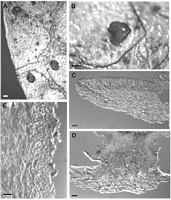
Caption: Fig. 3 Moellerodiscus griseliniae (A-B, PDD 64239; C-E,PDD 70062). A, macroscopic
appearance with apothecia in large, irregularly shaped stromatic areas; B, macroscopic
appearance, detail of a | 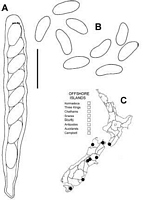
Caption: Fig. 4 Moellerodiscus griseliniae (PDD 70061). A, ascus containing ascospores; B, released
ascospores; C, distribution of collections examined. Scale bar A, B = 20 µm. |
Article: Johnston, P.R. (2002). Three new species of Moellerodiscus (Helotiales, Rutstroemiaceae) from New Zealand. New Zealand Journal of Botany 40(1): 105-115 (http://www.rsnz.org/publish/abstracts.php).
Description: DESCRIPTION: Apothecia developing on both upper and lower surface of fallen leaves,
associated with irregularly shaped stromatic areas (often with several areas on a single leaf),
leaf surface in these areas slightly blackened, margin marked by a narrow black zone line.
Apothecia erumpent from beneath epidermis, arising from basal stroma comprising textura
intricata of tightly packed hyphae c. 5 µm diam., with walls thick, gelatinous, dark brown,
with scattered groups of crystals 40-60 µm diam. at base of stroma and in surrounding host
tissue; hyphae within host tissue 5 µm diam. with walls gelatinous, hyaline, completely
replacing leaf tissue, except for the more or less intact epidermis and upper layer
of hypodermal cells. Apothecia up to 4 mm diam.,cupulate, short stipitate to stipitate; disc
plane, dark red when fresh, very dark red to black when dry; receptacle finely roughened,
concolorous with disc, when dry often with small, scattered clumps of bright rusty brown
material; stipe more or less cylindric, with black base. Ascomata release bright pinkish
red ("vivid Red", Kelly 1965) pigment in KOH. Ectal excipulum 50-65 µm thick, textura
globosa to textura angularis with elements oriented more or less perpendicular to receptacle
surface, comprising short-cylindric, angular or globose, 6-12 µm diam. cells with walls thick,
hyaline, refractive, with outermost cells 5-11.5 µm diam., more or less free,
containing red-brown pigment. Medullary excipulum textura intricata of loosely packed hyphae 3-4.5
µm diam. with walls thin, finely encrusted, pale brown, nongelatinous. Subhymenium a dense
textura intricata comprising hyphae 3-5 µm diam. with walls pale brown, thin to slightly
thickened, nongelatinous. Paraphyses 1.5-2 µm diam., apex slightly swollen to 3-4 µm diam.,
unbranched, about same length as asci. Asci (75-)80-100(-110) x (9.5-)10.5-11.5(-12) µm,
cylindric to subclavate, tapering slightly to subtruncate apex, wall thickened at apex, apical pore amyloid with small
but intense reaction on inside edge of wall, 8-spored, spores overlapping uniseriate, extending
70-75 µm from ascus apex. Ascospores (10.5-)11.5-12.5(-14) x (4.5-)5-6(-6.5) µm (x- 12 x
5.75 µm, n = 45), ovate to broad elliptic, more or less symmetrical, each end broadly rounded,
slightly curved, sometimes slightly wider in upper half, 0-septate, wall hyaline, thin,smooth.
Notes: ETYMOLOGY: Refers to host substrate.
NOTES: M. griseliniae is macroscopically similar to M. coprosmae (see Discussion and Table
1). Lanzia griseliniae, another discomycete which also occurs on fallen Griselinia leaves, does
not appear to be as common as C. griseliniae, although the two species can sometimes be
found at the same site. L. griseliniae differs in apothecial colour: when fresh the disc is
mustard-yellow and the receptacle pale yellow-brown, when dry the disc is more variable in
colour, from a blackish brown to deep orange brown (TAUPO: Tongariro National Park,
Ruapehu,on Griselinia littoralis, J. M. Dingley, 20 Oct 1949, PDD 19046. NELSON: vic.
Karamea, Kohaihai, Nikau Walk, on Griselinia lucida, P. R. Johnston D1041, 11 May 1994,
PDD 64240. STEWART ISLAND: Mason Bay, on Griselinia littoralis, P. R.Johnston D1406
& E. H. C. McKenzie, 11 May 1994,PDD 70058). The two species also differ in apothecial
structure, and ascospore size and shape (see description in Spooner 1987). Collections
very similar to L. griseliniae have also been found on Pseudopanax crassifolius, Metrosideros
excelsa, andM. umbellata (unpubl. data).
|