|
 Aleurina magnicellula Aleurina magnicellula
BiostatusPresent in region - Indigenous. Endemic
Images (click to enlarge)
Owner: J.A. Cooper | 
Owner: J.A. Cooper | 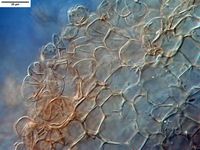
Caption: excipulum
Owner: J.A. Cooper | 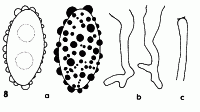
Caption: Fig. 8. Aleurina magnicellula a. ascospores, x1580; b. ascus bases, x1000; c. paraphysis apex, x1000; holotype. | 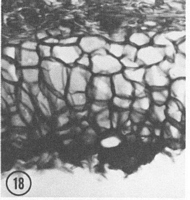
Caption: Fig. 18. Aleurina magnicellula: ectal excipulum, x220; holotype. | 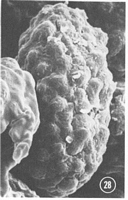
Caption: Fig. 21-30. SEM study of ascospores and spore markings. 28. A. magnicellula All x3000, all holotypes except Figs. 23, 24. |
Article: Zhuang, W.Y.; Korf, R.P. (1986). A monograph of the genus Aleurina Massee (= Jafneadelphus Rifai). Mycotaxon 26: 361-400.
Description: Apothecium discoid, sessile, up to 5-15 mm in diam when dry, hymenium olivaceous to
brown when fresh, brown to dark olivaceous brown when dry, receptacle surface light brown
to brown when fresh, dark brown when dry, with pustules. Ectal excipulum of textura
angularis, 120-260 µm thick, margin thicker, extended towards the outside up to 350 µm,
cells brownish, polygonally isodiametric to ellipsoid, cell walls rigid and more or less
thickened, 44-70(-83) x 25-44 µm, axes of cells perpendicular to the outer surface; cells of
pustules subspherical, brown, 14-26 µm in diam; basal hyphae pale brown to subhyaline, 4.5-7.5 µm wide.
Medullary excipulum of textura intricata, about 400 µm thick (up to 3 mm
thick according H. Dissing), hyphae pale brown, 5.0-10.0 µm wide, more or less parallel to
the outer surface. Subhymenium of textura intricata, 50-130 µm thick. Asci 8-spored,
cylindrical, sometimes with a tapered base inserted deeply into the subhymenlum, J- in
Melzer's Reagent, with crozier at base, 360-410 x 14.0-19.0 µm. Ascospores uniseriate,
ellipsoid, uniguttulate to biguttulate, 24.0-29.7 x 12.2-15.0 µm; spore markings usually
higher than hemispherical, up to 4.0 µm in diam and 3.0 µm high. Paraphyses slightly
enlarged at apex, 5.0-6.0 µm at apex, 4.0-4.5 µm below, with a dark blue cap in Soluble Blue
(Fig. 8c), not exceeding asci.
Notes: Notes: This species differs from A. ferruginea in the much larger and thicker-walled cells of the ectal
excipulum, the narrow and atypically shaped crozier at the ascus base, and the larger spore
markings, and from A. imaii in the larger and thicker-walled cells of the ectal excipulum, the
larger spore size, and the relatively smaller spore markings. The SEM study shows that the
membrane which covers the ascospore surface of this species is relatively thick and coarse
(Fig. 28).
|