|
 Coccomyces libocedri Coccomyces libocedri
BiostatusPresent in region - Indigenous. Endemic
Images (click to enlarge)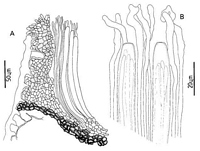
Caption: Fig. 9 Coccomyces libocedri: A, ascocarp margin in cross-section. B, apices of asci and
paraphyses. | 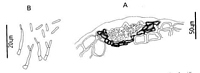
Caption: Fig. 10 Anamorph of Coccomyces libocedri: A, pycnidium in cross-section. B,
conidiogenous cells and conidia. | 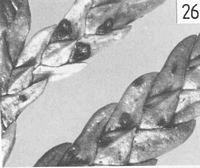
Caption: Fig. 26 Macroscopic appearance of ascocarp (x 12).
C. libocedri.
|
Article: Johnston, P.R. (1986). Rhytismataceae in New Zealand. 1. Some foliicolous species of Coccomyces de Notaris and Propolis (Fries) Corda. New Zealand Journal of Botany 24(1): 89-124 (http://www.rsnz.org/publish/abstracts.php).
Description: Ascocarps form in pale, brownish lesions on fallen leaves. Lesions not associated with zone
lines. Ascocarps ovate to oblong or irregular in outline, 0.6-0.8 x 0.4-0.5 mm diam. Walls
pale grey, no paler zones to indicate future lines of opening, darker around the outside edge.
Opening by several irregular, radiate slits, to expose the yellowish hymenium. Lip cells
absent. Pycnidia numerous, round, 0.2 mm diam., flat, pale walled, darker around the outer
edge and the single, round ostiole.
Ascocarp intraepidermal. In vertical section upper stromatal layer 15-20 µm wide,
comprising rounded, pale brown, thin walled cells. An extra laver of hyaline, gelatinous cells
developing between the upper stromatal layer and the covering host tissue. Lower stromatal
layer 15 µm wide, comprising 3-4 layers of dark brown, thick walled cells. Excipulum
absent.
Paraphyses 2 µm diam., becoming irregularly tangled and swollen up to 4.5µm diam. at
apices, extending 15-20 µm beyond asci. Asci cylindric, 195-235 x 9-10.5 µm, tapering
slightly to a broad, truncate apex, uniformly thin walled, non-amyloid, 8-spored. Ascospores
filiform, 142-206 x 1.8-2 µm, not tapering, 0-3 septate, surrounded by a poorly developed
gelatinous sheath.
Pycnidia intraepidermal, flat and lenticular in shape, upper wall absent. Lower wall 7-12 µm
wide, of 1-3 layers of dark brown, thick walled cells, 3-5 µm diam., lined with 1-2 layers of
hyaline cells, on which the conidiogenous layer forms. Conidiogenous cells 8-12 x 1.5-2
µm, solitary, cylindric to flask-shaped, sympodial. Conidia cylindric with rounded ends, 4-6
x 1 µm, hyaline, non-septate.
CHARACTERISTICS IN CULTURE: Ascospores germinating on agar plates after 48 h.
Cultures on oatmeal agar 3.5-4 cm diam. after 6 weeks; aerial mycelium tufted, pale grey, in
two concentric bands; agar surface undulate, dark brown in colour, fruiting bodies appear to
be forming near edges of colonies, but remaining sterile.
Habitat: Found only on dead leaves of Libocedrus bidwillii, still attached to the plant.
Notes: ETYMOLOGY: libocedri; refers to host plant.
NOTES: The ascocarp is similar in external appearance to C. cupressinum, but the two
species are easily distinguished microscopically. Lophodermium juniperi (Greville) Darker is
recorded from Libocedrus decurrens Torr. (Hunt & Ziller 1978).
This species has lip cells lining the single opening slip, asci 110-130 x 15-17 µm, and
ascospores 70-90 x 2-3 µm. Two species, described as Hypoderma by Butin (1970) from
Pilgerodendron species, have saccate asci and ascospores less than 50 µm long.
|