|
 Cheilymenia pallida Cheilymenia pallida
BiostatusPresent in region - Exotic
Images (click to enlarge)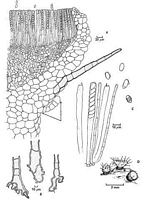
Caption: Fig. l. A-D, Cheilymenia pallida. A, Longitudinal section through a mature apothecium
(arrows indicate non-rooting hair), B, bases of rooting hairs; C, asci, ascopores and
paraphyses; D, habit sketch of three apothecia, one of which has few roo |
Article: Bell, A.E.; Dennis, R.W.G. (1971). Cheilymenia pallida sp. nov. from New Zealand. Transactions of the British Mycological Society 57(1): 180-182.
Description: Apothecia scattered or gregarious, 1.5-3 mm diameter. Disk flat, pale whitish-buff (code
5Y8/2 using the 'Standard Soil Color Chart' published by the Nippon Shikaisha Co. Ltd.,
Japan), receptacle a darker buff (2.5Y 7/4) shading to brown (2.5Y 6/6) at a stout base,
clothed at the top with stiff, brown, septate rooting hairs. The latter are variable in number
and sometimes apparently absent. However, microscopical examination of an apparently
hairless apothecium usually reveals septate, brown rooting hairs of greatly reduced size are
present. The bases of the rooting hairs are variable in shape, sometimes distinctly forked, as
in Cheilymenia coprinaria (Cooke) Boud., sometimes simple or bulbous (Fig. 1 B). Hyaline
hyphal outgrowths, composed of a chain of bulbous thin-walled cells are sometimes present
(Fig. l A). In quantity they form a loose tomentum radiating from the apothecium, giving it a
woolly appearance (Fig. 1 D). In such specimens brown rooting hairs are generally sparse.
The rooting hairs are straight, 200--800 µm long, approximately 40 µm in diameter at the
base tapering gradually to a sharp-pointed apex and having four to twenty-eight, thin,
transverse septa. The hair walls are dark brown (especially at the base), and approximately 4
µm thick. The ectal excipulum is built of large subglobose or polygonal cells, sharply
delineated from an inner medullary region of smaller, irregular cells interspersed with hyphae
of no obvious orientation (Fig. 1 A). A few larger cells in the outer medullary region have
contents which appear denser due to their ability to retain the staining material (safranin and
fast green). Asci cylindrical 185 x 8 µm, tapering to a narrow base with a bluntly rounded
apex, and containing eight uniseriately arranged ascospores. Ascospore oblong-ellipsoidal 8-12 x 5-6 µm, smooth walled, hyaline without oil globules and with a delicate outer wall
separable when heated in lactic acid (Fig. 1 C). Paraphyses 4 µm in diameter, with a few
septa, slightly enlarged apex and containing hyaline granules; carotinoid pigment not found.
Habitat: Habitat: faecal pellets of the brush-tailed opossum, Trichosurus vulpecula Kerr., collected on
the ground in indigenous lowland forests, Orongorongo Valley, near Wellington New
Zealand. In the laboratory, under humid conditions and at room temperatures (10-24 °C),
apothecia appear on pellets after an average of 24 incubation (range: 7-40 days).
|